
Despite its importance to terrestrial animals, water availability is rarely incorporated into multiple-stressor frameworks.

Multiple stressors may have additive or non-additive effects on fitness-related traits, such as locomotion, reproduction, and somatic growth. Many environmental stressors naturally covary, and the frequency and duration of stressors such as heat waves and droughts are increasing globally with climate change.
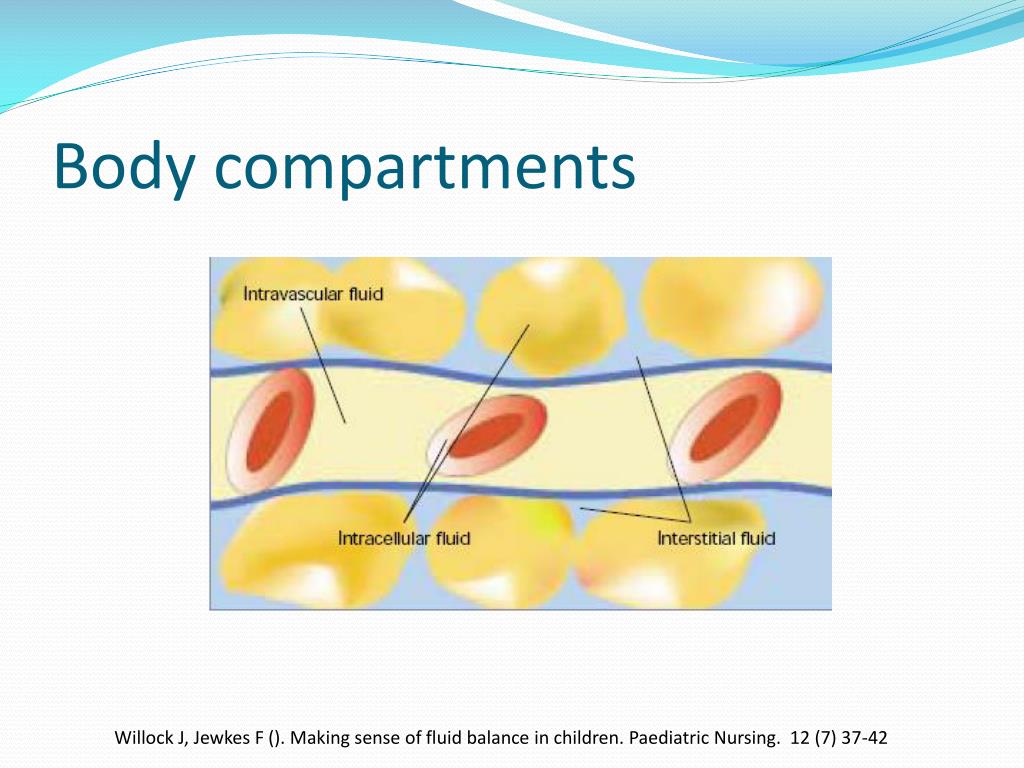
This will provide a good model for the study on the gut microbial differences in sympatric frogs. These species are distributed along mountain streams and congregate in large numbers during the breeding reason in mountain streams. These three Anura frogs are commonly observed on rocks near streams. Similar alpha diversity and interspecific bacterial similarity in the gut might be related to bacterial transmission among the three Anura frogs evaluated in this study. From these findings, that the relative abundance of the gut microbiota and predicted gene functions differed in three species, we conclude that there were significant differences in the gut microbiota of the three species. Metabolism‐related gene function was predominantly enriched in the gut microbiota of the three evaluated frog species. However, bacterial similarity of gut microbiota was significantly different between O. No differences were observed in alpha diversity indexes among the three frog species. The most dominant genera were Burkholderia, Caballeronia, and Paraburkholderia with the highest relative abundance in O. The most abundant family was Burkholderiaceae in three species. In these three frog species, the most abundant phylum was Proteobacteria, followed by Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, and Firmicutes. Here, 16S rRNA gene sequencing technology was employed to study the gut microbiota of three sympatric frog species, namely Odorrana tormota, O. The similarity of gut microbiota in related or sympatric species has been gaining recent traction. Collectively, isotocin seems to be a major circulating hormone that induces swallowing through its action on the AP, while AngII may be an intrinsic brain peptide that induces drinking through its action on a different circumventricular site, possibly a recently identified blood-brain barrier-deficient structure in the antero-ventral third ventricle of eels, as shown in birds and mammals.Ĭomposition and diversity in gut microbiota are impacted by a wide variety of factors. Lesioning of the area postrema (AP), a sensory circumventricular organ, abolished drinking induced by peripheral isotocin, but not i.c.v. By contrast, intra-cerebroventricular (i.c.v.) injection of isotocin had no effect on drinking or blood pressure, but AngII increased drinking and aortic pressure dose-dependently at 0.03-0.3 nmol/eel. The baroreceptor may exist distal to the gill circulation because the vasopressor effect occurred at both ventral and dorsal aorta after AngII but only at ventral aorta after isotocin. No such inhibition was observed after isotocin despite similar concurrent hypertension. By contrast, a sustained inhibition of drinking occurred after AngII, probably due to baroreflexogenic inhibition.
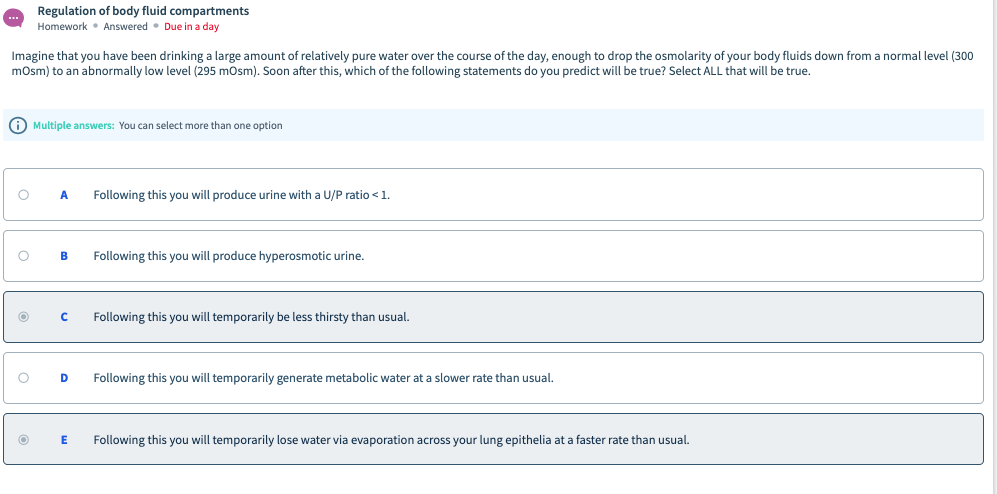

The dipsogenic effect was dose-dependent and occurred significantly at as low as 0.1 nmol/kg. When injected intra-arterially into conscious eels, isotocin, vasotocin and AngII equally increased ventral aortic pressure dose-dependently at 0.03-1.0 nmol/kg, but only isotocin induced copious drinking. In this study, we found that systemic isotocin, but not vasotocin, is the potent dipsogenic hormone in eels. Angiotensin II (AngII) is generally known as the most important dipsogenic hormone throughout vertebrates, while two other neurohypophysial hormones, vasopressin and oxytocin, are not dipsogenic in mammals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
